Multi-User Design
Out of date
This page is primarily included for historical reference, it explains the original design of Kubeflow’s multi-tenancy support. The current implementation has progressed significantly beyond the initial design.
For practical information about using multi-tenancy in Kubeflow, see Profiles and Namespaces.
Design overview
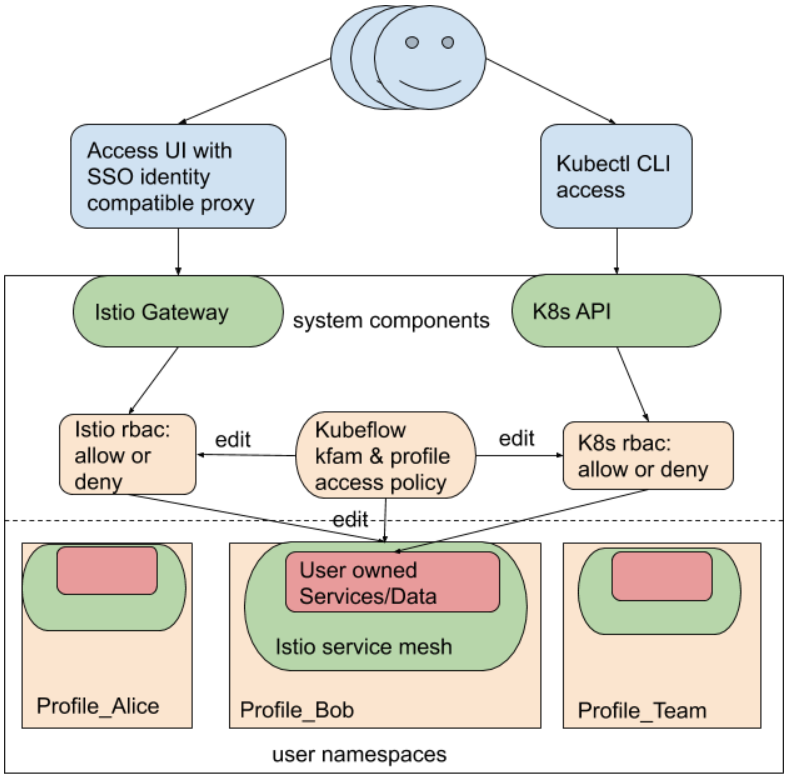
Kubeflow multi-tenancy is currently built around user namespaces. Specifically, Kubeflow defines user-specific namespaces and uses Kubernetes role-based access control (RBAC) policies to manage user access.
This feature enables users to share access to their workspaces. Workspace owners can share/revoke workspace access with other users through the Kubeflow UI. After being invited, users have permissions to edit the workspace and operate Kubeflow custom resources.
Kubeflow multi-tenancy is self-served - a new user can self-register to create and own their workspace through the UI.
Kubeflow uses Istio to control in-cluster traffic. By default, requests to user workspaces are denied unless allowed by Istio RBAC. In-bound user requests are identified using an identity provider (for example, Identity Aware Proxy (IAP) on Google Cloud or Dex for on-premises deployments), and then validated by Istio RBAC rules.
Internally, Kubeflow uses the Profile custom resource to control all policies, roles, and bindings involved, and to guarantee consistency. Kubeflow also offers a plugin interface to manage external resource/policy outside Kubernetes, for example interfacing with Amazon Web Services APIs for identity management.
The following diagram illustrates a Kubeflow multi-tenancy cluster with two user-access routes:
- via the Kubeflow central dashboard
- via the kubectl command-line interface (CLI)
Feature requirements
- Kubeflow uses Istio to apply access control over in-cluster traffic.
- Kubeflow profile controller needs
cluster adminpermission. - Kubeflow UI needs to be served behind an identity aware proxy. The identity aware proxy and Kubernetes master should share the same identity management.
- The Kubeflow installation on Google Cloud uses GKE and IAP.
- Default installations of Kubeflow make use of Dex, a flexible OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.